Authors: Wang Xiaoyan, Zhao Eryu
Unit: Jiaozhou Hospital, Dongfang Hospital Affiliated to Tongji University
At present, the main sample type for respiratory pathogen nucleic acid detection is throat swab. There are many kinds of commonly used sample preservation solutions, all of which need to be refrigerated or frozen for transportation and storage; It is difficult to control the whole process of low temperature during the collection and transportation process, and it is difficult to ensure the quality control before sample testing [1-2] .
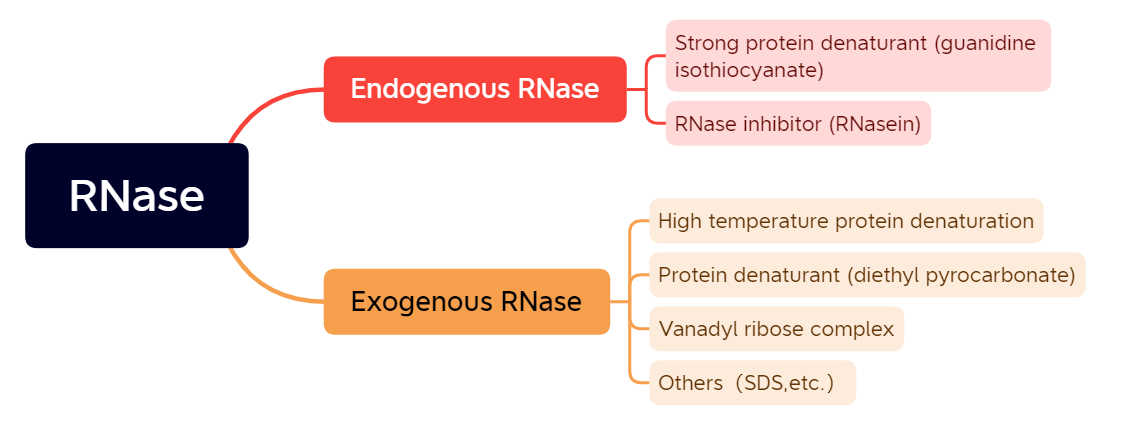
RNase (RNase) is an endonuclease that hydrolyzes RNA, mainly severing phosphodiester bonds between nucleotides. The RNase molecule is very stable, there are disulfide bonds in the structure, and its activity does not require the presence of divalent cations, so RNase is not easily denatured, and it is easy to renature even after high temperature or the use of denaturants. RNases are divided into endogenous and exogenous ones. The endogenous RNases can be released at the same time when cells are ruptured. Therefore, eliminating the role of endogenous RNases is a very critical step in the RNA extraction process. Exogenous RNases are widely distributed. RNases exist in the air, human skin, hair and saliva, which are important reasons for the easy degradation of RNA [3] .
Data query
CANS-CL02-A009 “Application of Medical Laboratory Quality and Competency Accreditation Guidelines in the Field of Molecular Diagnosis” in the technical requirements proposes that appropriate water quality standards should be formulated according to the application; Disposable airtight containers:
RNase/Classification
(1) RNase A
Ribonuclease A (RNase A), derived from bovine pancreas, is an endoribonuclease that can specifically attack the 3′ end of pyrimidine residues on RNA, cutting cytosine or uracil formed by adjacent nucleotides. Phosphodiester bond, the final product of the reaction is a 3′ pyrimidine nucleotide and an oligonucleotide with a 3′ pyrimidine nucleotide at the end.
(2) RNase T1
Ribonuclease T1 (RNase T1) is derived from Aspergillus orjzae, it specifically acts on the 3′-terminal phosphate of guanine, and the cleavage site is between the 3′ phosphate of guanine and the 5′ hydroxyl of adjacent nucleotides. The final product of the reaction is 3′guanylic acid and oligonucleotide fragments with 3′guanylic acid at the end.
(3) RNase H
Ribonuclease H (RNase H) was first discovered from calf thymus tissue, and its encoding gene has been cloned into Escherichia coli. It can specifically degrade DNA: RNA strands in RNA hybrid duplexes, resulting in oligonucleotides and mononucleotides with 3′-OH and 5′-monophosphate ends, it cannot degrade single- or double-stranded DNA or RNA.
RNase
Function and use
Ribonuclease can catalyze the degradation of ribonucleic acid (RNA) and can be synthesized artificially. Medicinal ointment is used topically to treat trauma and joint pain. According to reports, ribonuclease can change host cell metabolism, inhibit virus synthesis, inhibit the proliferation of influenza virus in vitro, and inhibit the formation of vaccinia and herpes virus in chicken embryos. Clinical use of ribonuclease daily intramuscular injection of 180 mg, beneficial to the treatment of epidemic encephalitis, ribonuclease can catalyze the degradation of ribonucleic acid (RNA), and can now be artificially synthesized. Medicinal ointment is used topically to treat trauma and joint pain. According to reports, ribonuclease can change host cell metabolism, inhibit virus synthesis, inhibit the proliferation of influenza virus in vitro, and inhibit the formation of vaccinia and herpes virus in chicken embryos. Clinical use of ribonuclease daily intramuscular injection of 180 mg is beneficial for the treatment of epidemic encephalitis.
RNase
Inhibitor Definition
Definition of RNase inhibitor unit: The amount of enzyme required to inhibit 50% of the activity of 5ng RNase A is one unit.
How RNase Inhibitors Work
Guanidine isothiocyanate:
Guanidine isothiocyanate is an organic compound with the molecular formula C2H6N4S. Mainly used in biological medicine, chemical reagents, etc. Guanidine isothiocyanate is a protein lysing agent, and it is often used as the main component of lysis solution in molecular diagnostic reagents. It can lyse tissue, destroy cell structure and dissociate nucleic acid from nucleoprotein, and has strong denaturation to RNase. It is the most effective RNase inhibitor at present.
TRIzol is a novel total RNA extraction reagent that can directly extract total RNA from cells or tissues. It contains substances such as phenol and guanidine isothiocyanate, which can rapidly disrupt cells and inhibit nucleases released by cells.
(However, the guanidine isothiocyanate is dangerous for lab researchers’ health.)
RNasin:
Acid glycoprotein extracted from rat liver or human blastoderm. Rnasin is a non-competitive inhibitor of RNase, which can bind to various RNases to inactivate them.
(More details:https://www.foreivd.com/foreasy-rnase-inhibitor-product/)
High temperature:
High temperature is also a common means of protein denaturation.
Diethylpyrocarbonate (DEPC):
DEPC is a strong but incomplete RNase inhibitor, which can inhibit RNase activity by combining with the amino acid imidazole ring of the RNase active group to denature proteins.
Vanadyl ribonucleoside complex:
A complex formed by vanadium oxide ions and nucleosides, which binds to RNase in the form of transition substances, which can almost completely inhibit the activity of RNase
other:
SDS, urea, diatomaceous earth, etc. also have a certain inhibitory effect on RNase.
Expert Reviews
Li Yujie Chief Technician
Director of Laboratory Department, Jiaozhou Hospital, Dongfang Hospital Affiliated to Tongji University
In order to prevent the biodegradation of exogenous RNase, masks, gloves and hats should be worn and replaced frequently during the RNA extraction process. All glassware must be baked in a drying oven at 200°C for more than 2 hours. Materials used for baking, such as plastic, need to be treated with DEPC water, and then washed with distilled water. The reagents or devices used for extraction, preservation and identification of RNA should be dedicated to RNA, and an independent RNA operation area should be set up.
references:
[1] Smith-Vaughan HC, Binks MJ, Beissbarth J, et al. Bacteria and viruses in the nasopharynx immediately prior to onset of acute lower respiratory infections in Indigenous Australian children[J]. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis,2018,37 (9): 1785-1794.
[2] Hospital Infection Control Branch of Chinese Preventive Medicine Association. Guidelines for the collection and inspection of clinical microbial specimens [J]. Chinese Journal of Hospital Infection, 2018(20):3192-3200.
[3] “Clinical Test Ten Thousand Why Molecular Biology Test Volume”
Post time: Aug-09-2022