Source: WuXi AppTec
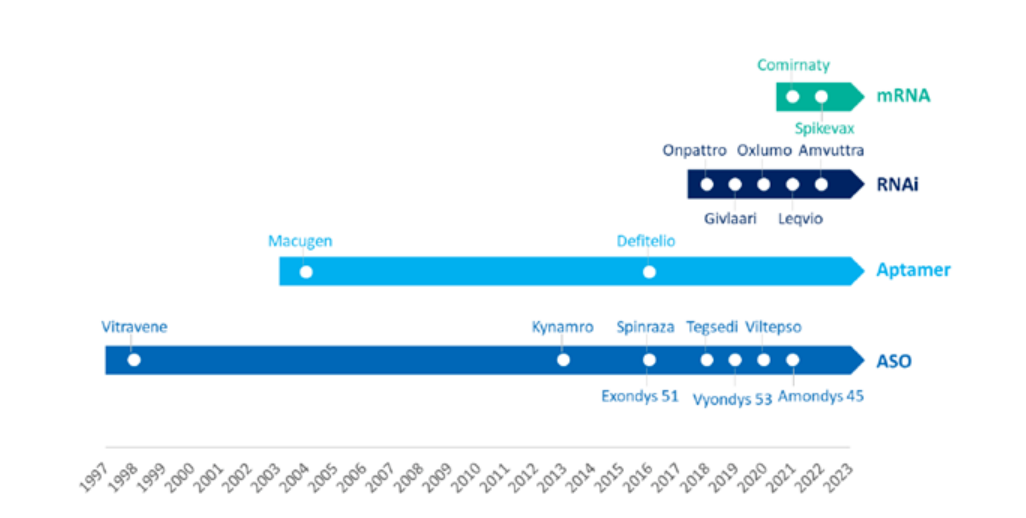
Recent years, the field of RNA therapy has shown an explosive trend- in the past 5 years alone, 11 RNA therapies have been approved by the FDA, and this number even exceeds the sum of previously approved RNA therapies! Compared with traditional therapies, RNA therapy can quickly develop targeted therapies with a higher success rate as long as the gene sequence of the target is known. On the other hand, most RNA therapies are still only available to treat rare diseases, and the development of such therapies still faces multiple challenges in terms of therapy durability, safety, and delivery. In today’s article, the content team of WuXi AppTec will review the progress in the field of RNA therapy in the past year, and look forward to the future of this emerging field with readers.
▲ 11 RNA therapies or vaccines have been approved by the FDA in the past 5 years
From rare diseases to common diseases, more flowers bloom
In the new crown epidemic, the mRNA vaccine was born out of nowhere and has received widespread attention from the industry. After the breakthrough in the development of infectious disease vaccines, another major challenge facing mRNA technology is to expand the scope of application for the treatment and prevention of more diseases.
Among them, individualized cancer vaccines are an important application field of mRNA technology , and we have also seen positive clinical results of several cancer vaccines this year. Just this month, the individualized cancer vaccine jointly developed by Moderna and Merck, combined with the PD-1 inhibitor Keytruda, reduced the risk of recurrence or death in patients with stage III and IV melanoma after complete tumor resection by 44% (compared to Keytruda monotherapy). The press release pointed out that this is the first time that an mRNA cancer vaccine has shown efficacy in the treatment of melanoma in a randomized clinical trial, which is a landmark event in the development of mRNA cancer vaccines.
In addition, mRNA vaccines can also enhance the therapeutic effect of cell therapy . For example, a study by BioNTech pointed out that if patients are first infused with a low dose of CLDN6-targeted CAR-T therapy BNT211 , and then injected with an mRNA vaccine encoding CLDN6, they can stimulate CAR-T cells in vivo by expressing CLDN6 on the surface of antigen-presenting cells. Amplification, thereby enhancing the anticancer effect. Preliminary results showed that 4 out of 5 patients who received the combination therapy achieved a partial response, or 80%.
In addition to mRNA therapy, oligonucleotide therapy and RNAi therapy have also achieved good results in expanding the scope of diseases. In the treatment of chronic hepatitis B, nearly 30% of patients cannot detect hepatitis B surface antigen and hepatitis B virus DNA in vivo after using the antisense oligonucleotide therapy bepirovirsen jointly developed by GSK and Ionis for 24 weeks. In some patients, even 24 weeks after stopping treatment, these markers of hepatitis B were still undetectable in the body.
Coincidentally, the RNAi therapy VIR-2218 jointly developed by Vir Biotechnology and Alnylam was combined with interferon α, and in phase 2 clinical trials, about 30% of chronic hepatitis B patients also failed to detect hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg). In addition, these patients developed antibodies against hepatitis B protein, showing a positive immune system response. Taking these results together, the industry points out that RNA therapy may be the key to a functional cure for hepatitis B.
This could be just the beginning of RNA therapy for common diseases. According to Alnylam’s R&D pipeline, it is also developing RNAi therapies for the treatment of hypertension, Alzheimer’s disease, and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, and the future is worth looking forward to.
Breaking through the bottleneck of RNA therapy delivery
The delivery of RNA therapy is one of the bottlenecks limiting its application. Scientists are also developing a variety of technologies to specifically deliver RNA therapy to organs and tissues other than the liver.
One of the potential methods is to “bind” therapeutic RNAs with tissue-specific molecules . For example, Avidity Biosciences recently announced that its technology platform can couple monoclonal antibodies to oligonucleotides to effectively bind siRNAs. sent to skeletal muscle . The press release pointed out that this is the first time that siRNA can be successfully targeted and delivered to human muscle tissue, which is a major breakthrough in the field of RNA therapy.
Image source: 123RF
In addition to antibody conjugation technology, a number of companies developing lipid nanoparticles (LNP) are also “upgrading” such carriers. For example , ReCode Therapeutic uses its unique Selective Organ Targeting LNP Technology (SORT) to deliver a variety of different types of RNA therapy to the lungs, spleen, liver and other organs. This year, the company announced the completion of a US$200 million Series B round of financing, with the venture capital departments of Pfizer, Bayer, Amgen, Sanofi and other large pharmaceutical companies participating in the investment. Kernal Biologics , which also received $25 million in Series A financing this year, is also developing LNPs that do not accumulate in the liver, but can deliver mRNA to target cells such as the brain or specific tumors.
Orbital Therapeutics , which debuted this year, also takes the delivery of RNA therapy as a key development direction. By integrating RNA technology and delivery mechanisms, the company expects to build a unique RNA technology platform that can extend the persistence and half-life of innovative RNA therapeutics and deliver them to a variety of different cell and tissue types.
A new type of RNA therapy emerges at the historic moment
As of December 21 this year, in the field of RNA therapy, there have been 31 early-stage financing events (see the methodology at the end of the article for details), involving 30 cutting-edge companies (one company has received financing twice), with a total financing amount of 1.74 billion US dollars. The analysis of these companies shows that investors are more optimistic about those cutting-edge companies that are expected to solve many challenges of RNA therapy, in order to fully realize the potential of RNA therapy and benefit more patients.
And there are up-and-coming companies developing entirely new types of RNA therapeutics. Unlike traditional oligonucleotides, RNAi or mRNA, the new types of RNA molecules developed by these companies are expected to break through the bottleneck of existing therapies.
Circular RNA is one of the hot spots in the industry. Compared with linear mRNA, the circular RNA technology developed by a cutting-edge company called Orna Therapeutics can avoid being recognized by the innate immune system and exonucleases, which not only significantly reduces immunogenicity, but also has higher stability. In addition, compared with linear RNA, the folded conformation of circular RNA is smaller, and more circular RNA can be loaded with the same LNP, improving the delivery efficiency of RNA therapy. These features could help improve the potency and durability of RNA therapeutics.
This year, the company completed a US$221 million Series B round of financing, and also reached a research and development cooperation with Merck of up to US$3.5 billion . In addition, Orna also uses circular RNA to directly generate CAR-T therapy in animals, completing a proof of concept .
In addition to circular RNA, self-amplifying mRNA (samRNAs) technology has also been favored by investors. This technology is based on the self-amplification mechanism of RNA viruses, which can induce the replication of samRNA sequences in the cytoplasm, prolonging the expression kinetics of mRNA therapeutics, thereby reducing the frequency of administration. Compared with traditional linear mRNA, samRNA is able to maintain similar protein expression levels at approximately 10-fold lower doses. This year, RNAimmune , which focuses on the development of this field, received US$27 million in Series A financing.
tRNA technology is also worth looking forward to. The tRNA-based therapy can “ignore” the wrong stop codon when the cell makes the protein, so that the normal full-length protein is produced. Because there are far fewer types of stop codons than associated diseases, tRNA therapy has the potential to develop a single therapy that can treat many diseases. This year, hC Bioscience , which focuses on tRNA therapy, has raised a total of US$40 million in Series A financing.
Epilogue
As an emerging treatment model, RNA therapy has achieved rapid development in recent years, and many therapies have been approved. From the latest developments in the industry, it can be seen that cutting-edge RNA therapies are expanding the range of diseases that such therapies can treat, overcoming various bottlenecks in targeted delivery, and developing new RNA molecules to overcome the limitations of existing therapies in terms of efficacy and durability. multiple challenges. In this new era of RNA therapy, these cutting-edge companies may become the focus of the industry in the next few years.
Related products:
https://www.foreivd.com/cell-direct-rt-qpcr-kit-taqman-product/
https://www.foreivd.com/cell-direct-rt-qpcr-kit-direct-rt-qpcr-series/
Post time: Dec-27-2022