PCR is the most widely used nucleic acid amplification technology and is widely used due to its sensitivity and specificity. However, PCR requires repeated thermal denaturation and cannot get rid of the limitations of relying on instruments and equipment, which limits its application in clinical field testing.
Since the early 1990s, many laboratories have begun to develop constant temperature amplification technology that does not require thermal denaturation. Now they have developed loop-mediated isothermal amplification technology, strand replacement isothermal amplification technology, rolling circle isothermal amplification technology, and nucleic acid sequence dependence. Isothermal amplification technology and other technologies.
Loop-mediated isothermal amplification
The amplification principle is based on the fact that DNA is in a dynamic equilibrium state at about 65°C. When any primer is base-paired and extended to the complementary part of double-stranded DNA, the other strand will dissociate and become single-stranded.
At this temperature, DNA uses 4 specific primers to rely on a strand-displacement DNA polymerase to make the synthesis of strand-displacement DNA self-circulate continuously.
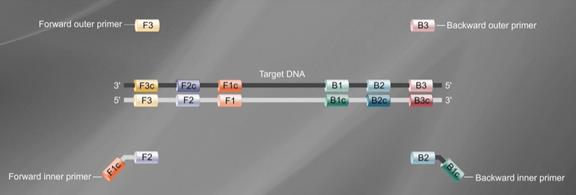
First determine the 6 specific regions F3, F2, F1, B1, B2, B3 on the target gene, and then design 4 primers based on these 6 specific regions (as shown in the figure below):
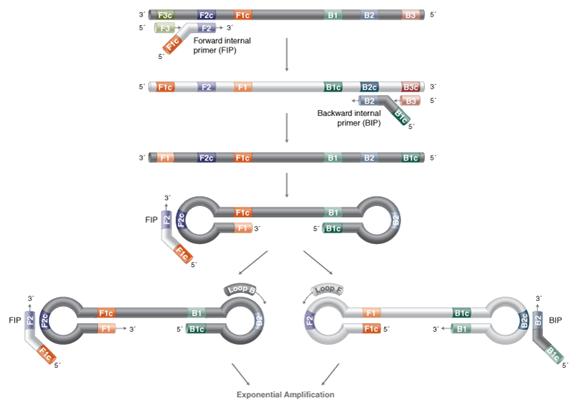
The forward inner primer (FIP) is composed of F1c and F2.
The backward inner primer (BIP) is composed of B1c and B2, and TTTT is used as a spacer in the middle.
The outer primers F3 and B3 are respectively composed of F3 and B3 regions on the target gene.
In the LAMP reaction system, the concentration of the inner primer is several times that of the outer primer. The inner primer is first combined with the template strand to synthesize a complementary strand to form a DNA double strand. Subsequently, the outer primer is combined with the template strand to form a DNA double strand. Under the action of BstDNA polymerase, the complementary strand synthesized by the inner primer is released. After a series of reactions, the complementary strand finally forms a single DNA strand with a dumbbell structure.
The dumbbell structure DNA single strand itself is used as a template to continuously form a transitional stem-loop structure DNA with an open end. The inner and outer primers guide the transitional stem-loop structure DNA to continuously undergo strand displacement and extension reactions, and finally form multiple stem-loop structures with different lengths. DNA mixture.
Advantages and disadvantages of loop-mediated isothermal amplification
Advantages of LAMP:
(1) High amplification efficiency, which can effectively amplify 1-10 copies of the target gene within 1h, and the amplification efficiency is 10-100 times that of ordinary PCR.
(2) The reaction time is short, the specificity is strong, and no special equipment is required.
Shortcomings of LAMP:
(1) The requirements for primers are particularly high.
(2) The amplified product cannot be used for cloning and sequencing, but can only be used for judgment.
(3) Due to its strong sensitivity, it is easy to form aerosols, causing false positives and affecting the test results.
Strand displacement amplification
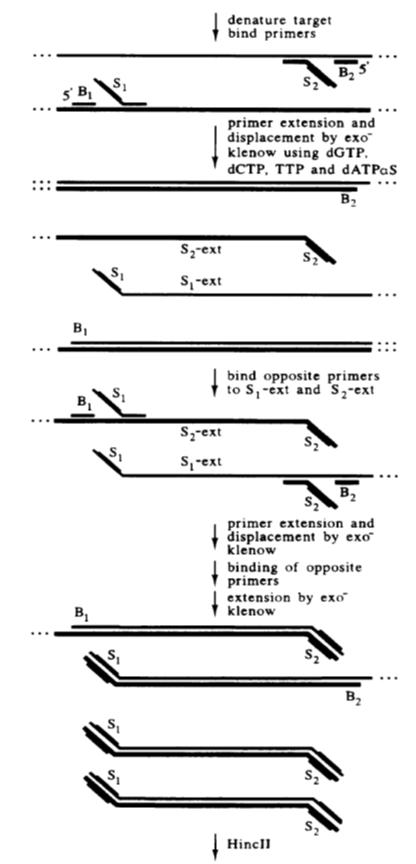
Strand displacement amplification (SDA) is an in vitro isothermal DNA amplification technique based on enzymatic reaction first proposed by American scholar Walker in 1992.
The basic system of SDA includes a restriction endonuclease, a DNA polymerase with strand displacement activity, two pairs of primers, dNTPs, and calcium and magnesium ions and buffer systems.
The principle of strand displacement amplification is based on the chemically modified restriction endonuclease recognition sequence at both ends of the target DNA. The endonuclease opens the gap in the strand DNA at its recognition site, and the DNA polymerase extends the gap 3′ End and replace the next DNA strand.
The replaced single strands of DNA can be combined with primers and extended into double strands by DNA polymerase. This process is repeated continuously, so that the target sequence is efficiently amplified.
Advantages and disadvantages of strand displacement amplification technology
Advantages of SDA:
The amplification efficiency is high, the reaction time is short, the specificity is strong, and no special equipment is required.
Shortcomings of SDA:
The products are not uniform, and some single-stranded and double-stranded products are always produced in the SDA cycle, and tailing will inevitably occur when detected by electrophoresis.
Rolling circle amplification
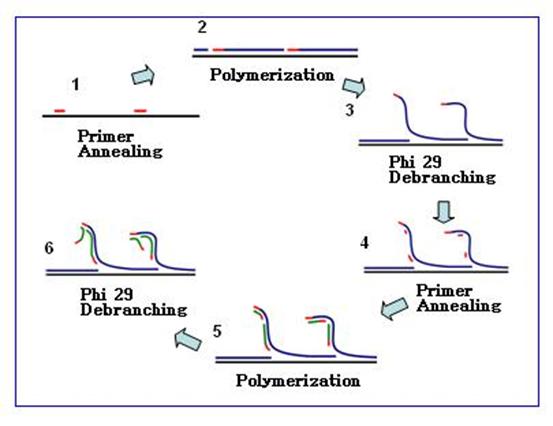
Rolling circle amplification (RCA) is proposed by drawing on the method of copying DNA from pathogenic organisms by rolling circle. It refers to the use of single-stranded circular DNA as a template at a constant temperature, and a special DNA polymerase (such as Phi29) ) Under the action of rolling circle DNA synthesis to achieve the amplification of the target gene.
RCA can be divided into linear amplification and exponential amplification. The efficiency of linear RCA can reach 105 times, and the efficiency of exponential RCA can reach 109 times.
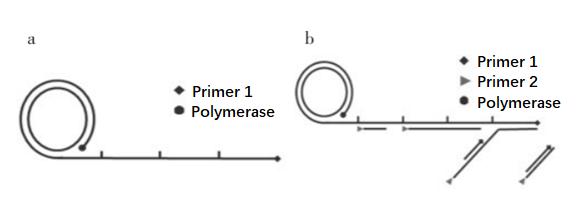
Simple distinction, as shown in the figure below, linear amplification a only uses 1 primer, exponential amplification b has 2 primers.
Linear RCA is also called single primer RCA. A primer binds to circular DNA and is extended by the action of DNA polymerase. The product is a linear single strand with a large number of repetitive sequences thousands of times the length of a single loop.
Since the product of linear RCA is always connected to the starting primer, the easy fixation of the signal is a major advantage.
Exponential RCA, also known as Hyper branched amplification HRCA (Hyper branched RCA), in exponential RCA, one primer amplifies the RCA product, the second primer hybridizes with the RCA product and extends, and the replacement is already bound to the RCA product The downstream primers extend the strand, and repeat extension and replacement to produce a dendritic RCA amplification product.
The advantages and disadvantages of rolling circle nucleic acid amplification
Advantages of RCA:
High sensitivity, good specificity and easy operation.
Shortcomings of RCA:
Background problems during signal detection. During the RCA reaction, the uncirculated padlock probe and the template DNA or RNA of the unbound probe may generate some background signals.
Nucleicacid sequence-based amplification
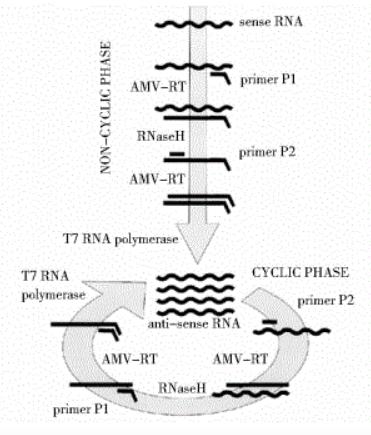
Nucleic acid sequence-based amplification (NASBA) is a new technology developed on the basis of PCR. It is a continuous and isothermal nucleic acid amplification guided by a pair of primers with a T7 promoter sequence. The technology can amplify the template RNA by about 109 times in about 2 hours, which is 1000 times higher than the conventional PCR method and does not require special equipment.
This technology has been used for rapid diagnosis of diseases as soon as it appeared, and many companies currently use this method in RNA detection kits.
Although RNA amplification can also use reverse transcription PCR technology, NASBA has its own advantages: it can be carried out under relatively constant temperature conditions, and it is more stable and accurate than traditional PCR technology.
The reaction is at 41 degrees Celsius and requires AMV (avian myeloblastosis virus) reverse transcriptase, RNase H, T7 RNA polymerase and a pair of primers to complete.
The process mainly includes:
The forward primer contains the complementary sequence of the T7 promoter. During the reaction, the forward primer binds to the RNA strand and is catalyzed by the AMV enzyme to form a DNA-RNA double strand.
RNase H digests the RNA in the hybrid double-strand and retains the single-stranded DNA.
Under the action of the reverse primer and the AMV enzyme, a DNA double strand containing the T7 promoter sequence is formed.
Under the action of T7 RNA polymerase, the transcription process is completed and a large amount of target RNA is produced.
Advantages of NASBA:
(1) Its primer has a T7 promoter sequence, but the foreign double-stranded DNA has no T7 promoter sequence and cannot be amplified, so this technology has high specificity and sensitivity.
(2) NASBA directly incorporates the reverse transcription process into the amplification reaction, shortening the reaction time.
Disadvantages of NASBA:
(1) The reaction components are more complicated.
(2) Three kinds of enzymes are required to make the reaction cost higher.
Post time: Aug-06-2021