Real Time PCR, also known as quantitative PCR or qPCR, is a method for real-time monitoring and analysis of PCR amplification products.
Because quantitative PCR has the advantages of simple operation, fast and convenient, high sensitivity, good repeatability, and low contamination rate, it is widely used in medical testing, drug efficacy assessment, gene expression research, transgenic research, gene detection, pathogen detection, animal and plant detection. , food testing and other fields.
Therefore, whether you are engaged in basic research in life sciences, or employees of pharmaceutical companies, animal husbandry companies, food companies, or even employees of entry-exit inspection and quarantine bureaus, environmental monitoring departments, hospitals and other units, you will be more or less exposed to Or you need to know the knowledge of mastering quantitative PCR.
Principle of Real Time PCR
Real Time PCR is a method in which fluorescent substances are added to the PCR reaction system, and the fluorescence signal intensity in the process of PCR reaction is monitored in real time by a quantitative PCR instrument, and finally the experimental data is analyzed and processed.
【Amplification curve】 is the curve describing the dynamic process of PCR. The amplification curve of PCR is not actually a standard exponential curve, but a sigmoid curve.
[Platform phase of amplification curve] With the increase of the number of PCR cycles, the inactivation of DNA polymerase, the depletion of dNTPs and primers, and the inhibition of the synthesis reaction by the reaction by-product pyrophosphate, etc., the PCR does not always expand exponentially. , and will eventually enter a plateau.
[Exponential Growth Region of Amplification Curve] Although the plateau phase varies greatly, in a certain region of the exponential growth region of the amplification curve, the repeatability is very good, which is very important for quantitative analysis of PCR.
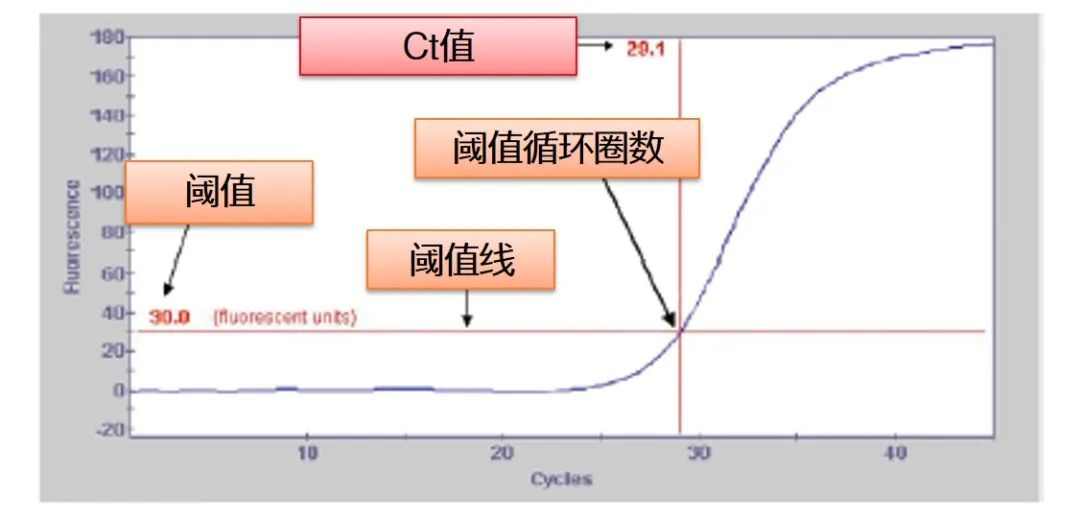
[Threshold value and Ct value] We set the limit value of fluorescence detection at the appropriate position in the exponential growth area of the amplification curve, namely the threshold value (Threshold). The intersection of the threshold value and the amplification curve is the Ct value, that is, the Ct value refers to the number of cycles (Threshold Cycle) when the threshold value is reached.
The graph below clearly shows the relationship between threshold line and amplification curve, threshold and Ct value.
【How to quantify? 】
It has been proved by mathematical theory that the Ct value has an inverse linear relationship with the logarithm of the number of initial templates. Real Time PCR monitors PCR amplification products in real time and quantifies them during the exponential amplification phase.
For each cycle of PCR, the DNA increased exponentially by 2 times, and soon reached a plateau.
Assuming that the amount of starting DNA is A 0 , after n cycles, the theoretical amount of DNA product can be expressed as:
A n =A 0 ×2 n
Then, the more the initial DNA amount A 0 is, the sooner the amount of the amplified product reaches the detection value An , and the number of cycles when reaching An is the Ct value. That is, the more the initial DNA amount A 0 is, the earlier the amplification curve peaks, and the correspondingly the required number of cycles n is smaller.
We carry out gradient dilution of the standard of known concentration and use it as a template for Real Time PCR, and a series of amplification curves will be obtained at equal intervals in the order of starting DNA amount from more to less. According to the linear relationship between the Ct value and the logarithm of the number of starting templates, a [standard curve] can be created .
By substituting the Ct value of the sample with unknown concentration into the standard curve, the initial template amount of the sample with unknown concentration can be obtained, which is the quantitative principle of Real Time PCR.
Detection method of Real Time PCR
Real Time PCR detects PCR amplification products by detecting the fluorescence intensity in the reaction system.
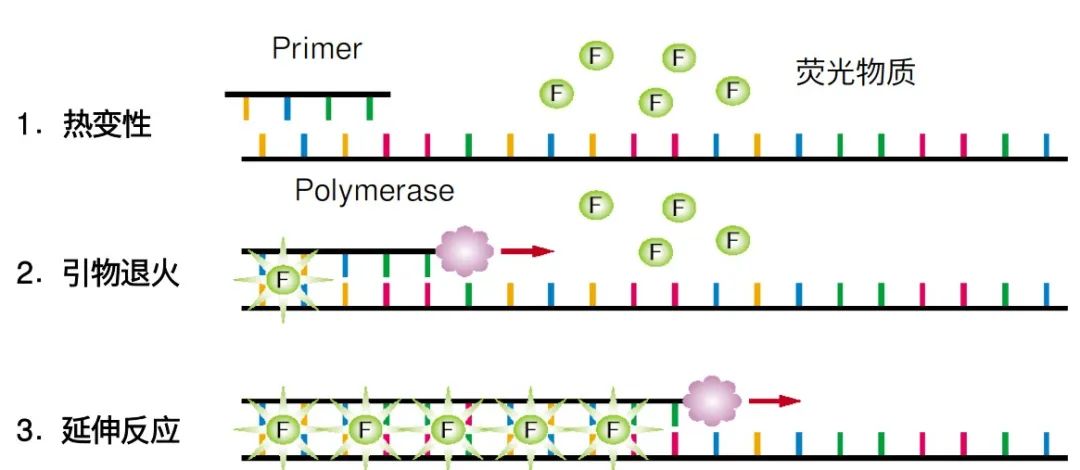
Principle of Fluorescent Dye Embedding Method】
Fluorescent dyes , such as TB Green ® , can nonspecifically bind to double-stranded DNA in PCR systems and fluoresce upon binding.
The fluorescence intensity in the reaction system increased exponentially with the increase of PCR cycles. By detecting the fluorescence intensity, the amount of DNA amplification in the reaction system can be monitored in real time, and then the amount of the starting template in the sample can be reversely estimated.
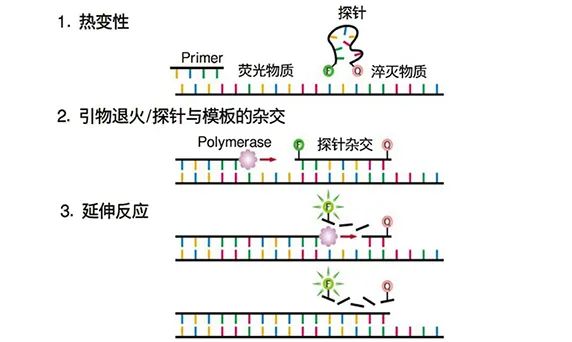
【Principle of fluorescent probe method】
fluorescent probe is a nucleic acid sequence with a fluorescent group at the 5′ end and a quenching group at the 3′ end, which can specifically bind to the template. When the probe is intact, the fluorescence emitted by the fluorophore is quenched by the quenching group and cannot fluoresce. When the probe is decomposed, the fluorescent substance will dissociate and emit fluorescence.
A fluorescent probe is added to the PCR reaction solution. During the annealing process, the fluorescent probe will bind to the specific position of the template. During the extension process, the 5′→3′ exonuclease activity of the PCR enzyme can decompose the fluorescent probe hybridized with the template, and the fluorescent substance is dissociated to emit fluorescence. By detecting the fluorescence intensity of the probe in the reaction system, the purpose of monitoring the amplification amount of the PCR product can be achieved.
【Selection of Fluorescence Detection Method】
If it is used to distinguish sequences with high homology and perform multiplex PCR detection such as SNP typing analysis, the fluorescent probe method is irreplaceable.
For other Real Time PCR experiments, a simple, easy and low-cost fluorescent chimera method can be used.
|
Dye method |
Probe method |
|
|
Advantage |
Simple, low cost, no need to synthesize specific |
probesStrong specificity, capable of multiplex PCR
Shortcoming
High specificity requirements for amplification;
multiplex PCR cannot be performedNeed to design specific probes, high cost;
sometimes probe design is difficult
Related Products:
Post time: Aug-18-2022